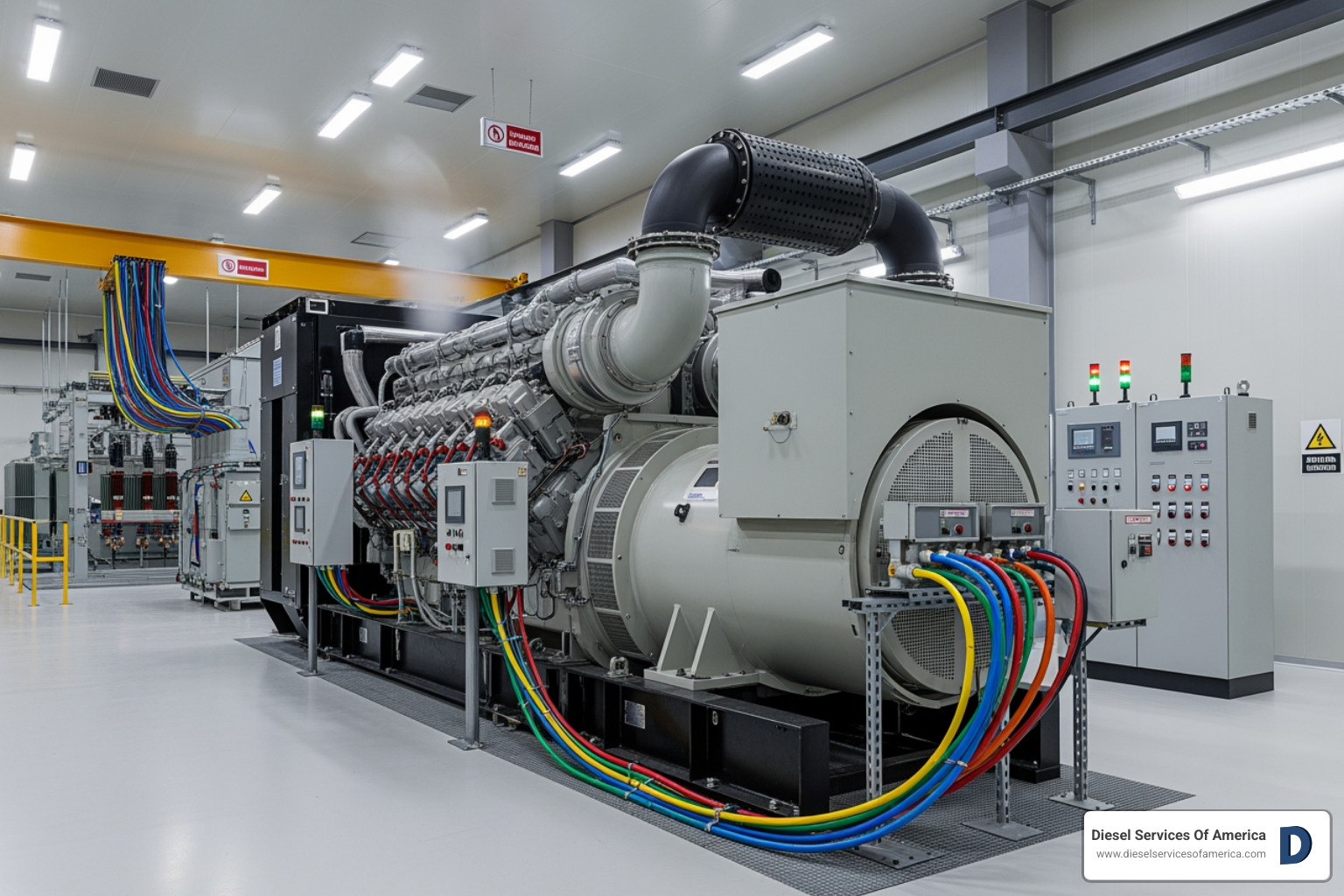
Why Diesel Engine Power Generation Powers Critical Operations
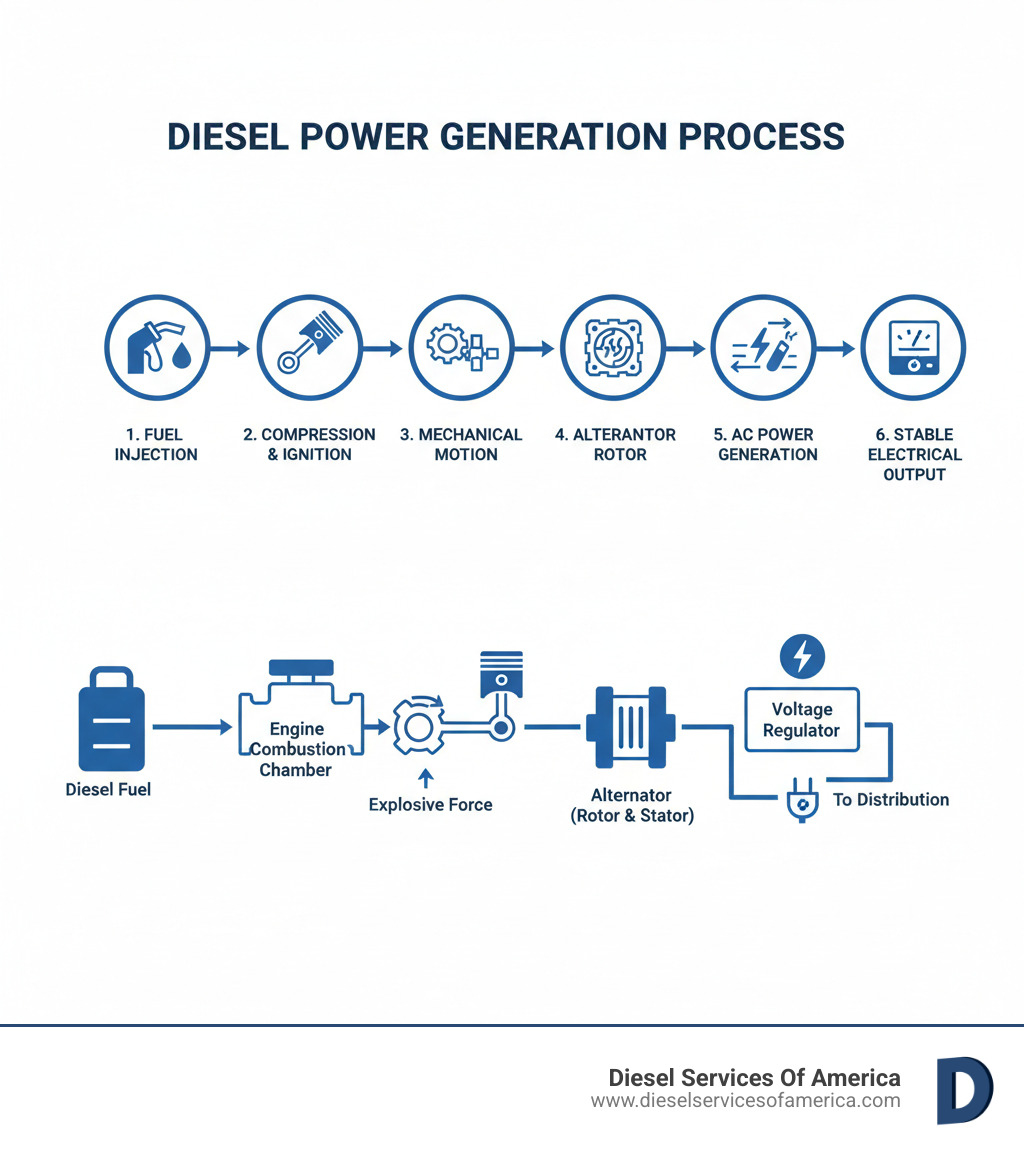
Diesel engine power generation is the process of converting chemical energy stored in diesel fuel into mechanical energy through combustion, which then drives an alternator to produce electrical power. This technology serves as the backbone of reliable electricity for critical facilities, remote operations, and marine vessels worldwide.
How Diesel Generators Work:
- Combustion – Diesel fuel ignites under high compression in the engine cylinders
- Mechanical Conversion – Pistons convert explosive force into rotational motion via the crankshaft
- Electrical Generation – The rotating crankshaft drives an alternator that produces AC electricity through electromagnetic induction
- Power Regulation – Voltage regulators ensure stable, usable electrical output
Our world depends on uninterrupted power. Communications, commerce, and safety systems all require 24/7 electricity. Yet power outages in the U.S. are up 64% in the last decade, costing the economy $150 billion annually. For a hospital, data center, or marine vessel, even momentary power loss can have severe consequences.
This is where diesel generators excel. Unlike grid-dependent systems, diesel generators provide self-contained, immediate power. They start in seconds, deliver full strength instantly, and run for extended periods. For marine applications—from luxury yachts to commercial fishing vessels—diesel generators function as critical secondary engines, drawing from the main fuel tank to power all electrical systems when the primary engine isn’t running.
The technology has evolved dramatically. Modern diesel generators emit 26 times less particulate matter than units from just a decade ago. High-quality engines now run 20,000-30,000 hours before their first overhaul. And with renewable diesel fuels, you can reduce your carbon footprint by 50-85% while maintaining the reliability diesel is known for.
Whether you’re managing a fleet of vessels in Southeast Florida or maintaining an industrial facility, understanding how diesel engine power generation works helps you make informed decisions about your critical power needs.
Essential Diesel engine power generation terms:
- Diesel engine efficiency improvements
- Diesel engine fuel consumption
- Diesel engine oil analysis
How Diesel Engine Power Generation Works: From Fuel to Electricity
The process of diesel engine power generation is a carefully orchestrated conversion of fuel and air into the electricity that powers your vessel or facility. Let’s walk through how it happens.
The Combustion Cycle: Igniting the Power
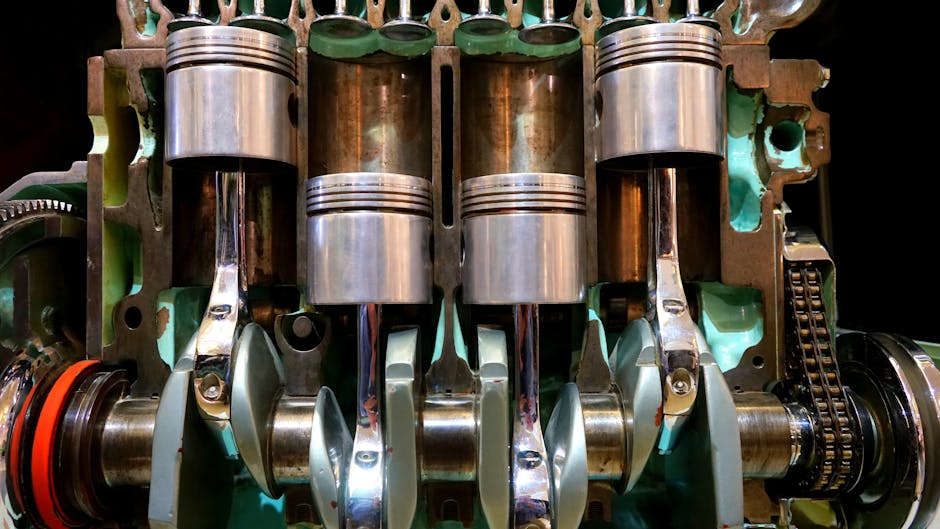
Everything starts with the four-stroke cycle inside the engine cylinders, a precisely timed sequence that repeats thousands of times per minute.
During intake, the piston pulls fresh air into the cylinder. Then comes compression, where the piston squeezes the air into a fraction of its original space. This compression creates so much heat and pressure that spark plugs are not needed.
At the peak of compression, a fine mist of atomized diesel fuel is injected into the superheated air. The fuel ignites spontaneously in what’s called compression ignition. This controlled explosion is the power stroke, converting chemical energy into mechanical force and driving the piston down with tremendous power.
Finally, the exhaust stroke pushes out the spent gases, and the cycle repeats. This continuous rhythm keeps your generator running smoothly for your commercial fishing vessel or industrial facility.
Mechanical to Rotational Energy Conversion
The pistons’ up-and-down motion must be converted into spinning motion to generate electricity.
Each piston connects to the crankshaft via a connecting rod. As the piston moves downward during the power stroke, it forces the crankshaft to rotate. This converts the piston’s linear motion into rotational energy.
A heavy flywheel attached to the crankshaft smooths out the pulses from each piston, creating steady rotation. This mechanical energy transfer prepares for the final conversion to electricity.
Generating Current Through Electromagnetic Induction
The spinning crankshaft drives the alternator, which converts this mechanical rotation into electrical current.
The alternator has two main components: the stator, a stationary housing with copper wire coils, and the rotor, an electromagnet that spins inside it on the same shaft as the crankshaft.
As the rotor spins inside the stator, its magnetic field sweeps across the copper coils. According to Faraday’s Law of Induction, moving a magnetic field past a conductor creates an electrical current. This results in AC voltage generation from the stator coils.
The faster your engine spins and the stronger the magnetic field, the more electricity you produce. It’s the same principle that powers everything from massive industrial generators to the compact units on marine vessels.
For a closer look at these essential components, check out More info about Diesel Generator Parts.
Ensuring Stable and Usable Power
Raw electricity straight from the alternator isn’t quite ready for prime time. Engine speed variations and changing electrical loads can cause voltage to bounce around, which is terrible for sensitive electronics.
The Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) is a smart device that constantly monitors the output. It adjusts the excitation current to the rotor’s electromagnet, strengthening or weakening the magnetic field as needed. The result is a rock-solid, stable voltage output regardless of the load.
Frequency regulation is handled by the engine’s governor, which fine-tunes fuel delivery to maintain constant engine speed. Since alternator frequency is directly tied to engine RPM, keeping that speed steady ensures your electricity stays at the proper 60 Hz (or 50 Hz internationally).
Once the AVR and governor have done their jobs, clean, stable, usable electricity flows through the power distribution panel. This regulated power keeps everything from data centers to yacht navigation systems running smoothly.
This entire process—from fuel injection to finished electricity—happens in milliseconds, cycling continuously to provide the reliable diesel engine power generation that keeps critical marine and industrial operations running 24/7.
Types, Ratings, and Key Applications of Diesel Generators
Diesel generators are not all the same. The design, size, and capabilities of diesel engine power generation systems vary dramatically based on their intended application. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right equipment for your facility in Fort Lauderdale or your yacht in the Caribbean.
Classifying Diesel Engines for Power Generation
Diesel engines for power generation are classified by engine speed, cooling method, and design. Each combination suits different applications, and knowing the differences can save you money and headaches.
| Feature | Air-cooled | Water-cooled | High-Speed (1500+ RPM) | Medium-Speed (500-1500 RPM) | Low-Speed (under 500 RPM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling | Air | Liquid (coolant) | Liquid/Air | Liquid | Liquid |
| Size | Smaller, portable, light industrial | Larger, industrial, marine, continuous duty | Compact, for quick response | Moderate, for industrial/prime power | Very large, heavy, for large-scale power plants/marine |
| Application | Small portable units, light-duty backup | Industrial facilities, marine vessels, data centers | Portable generators, quick-start applications | Larger industrial, prime power applications | Large power plants, marine propulsion, continuous operation |
| Efficiency | Less efficient for heavy, prolonged loads | More efficient for heavy, long-duration loads | Good for quick response, but higher wear | Balanced efficiency, durability, and fuel consumption | Highly durable, very efficient, long lifespan |
| Noise | Can be louder, especially smaller units | Generally quieter due to liquid dampening | Varies, often requires sound attenuation | Moderate noise levels | Lower noise relative to their immense power output |
Air-cooled engines are smaller and more portable, suitable for light industrial backup. They are simpler but less efficient for heavy, prolonged loads than water-cooled engines.
Water-cooled engines are the workhorses for industrial and marine use. Their liquid cooling systems handle heat effectively, making them ideal for extended operation and high power demands. For serious power output or long run times, water cooling is essential.
Engine speed also matters. High-speed engines (1500+ RPM) are compact and responsive, excellent for quick-start backup applications. Medium-speed engines (500-1500 RPM) balance efficiency, durability, and fuel consumption, making them popular for prime power in industrial settings. Low-speed engines (under 500 RPM) are durable, efficient giants for continuous large-scale operations like marine propulsion.
Most marine and industrial applications we work with rely on four-stroke engines, though you’ll occasionally find two-stroke designs in specialized marine propulsion systems. Four-stroke engines offer better fuel efficiency and lower emissions, which is why they dominate the market today.
Curious about what models might work for your operation? Check out our New Generator and Engine Sales to see what’s available.
Understanding Generator Ratings and Sizing
Generator ratings are precise specifications, not just marketing jargon, that determine how your generator should be used. Understanding them is crucial to avoid costly mistakes.
Standby Power (ESP) Rating generators are your emergency backup. They’re designed to kick in when the grid fails and run until utility power returns. Think hospitals during a hurricane or data centers during a blackout. These units aren’t meant for daily operation—they’re your insurance policy, ready to act when disaster strikes.
Prime Power (PRP) Rating generators are built for the long haul. If you’re operating in a remote location without reliable grid access, these are your primary power source. They can run continuously with varying loads, typically handling a 10% overload for short periods. Many industrial sites in the Caribbean and remote facilities rely entirely on prime-rated generators.
Continuous Power (COP) Rating units are the marathon runners of the generator world. They’re designed for 24/7 operation at constant load levels, never taking a break. You’ll find these in manufacturing plants or utility applications where consistent power output is non-negotiable.
Sizing your generator properly requires careful calculation. We look at your total electrical load (kW and kVA), the type of load (motors have different starting requirements), your intended application (standby, prime, or continuous), and environmental factors like altitude and ambient temperature. Fort Lauderdale’s heat and humidity, for instance, affect performance differently than conditions in the northern Caribbean.
Get the sizing wrong, and you’ll either waste money on an oversized unit or damage an undersized one. That’s why we take sizing seriously.
Primary Applications in Industrial and Marine Sectors
Diesel engine power generation powers the critical operations that keep our world running. Let’s look at where these systems make the biggest difference.
For standby power, diesel generators are irreplaceable. When Hurricane season threatens South Florida, hospitals, data centers, and telecommunications facilities count on diesel backup to maintain operations. With power outages increasing 64% over the last decade, having reliable standby power isn’t optional—it’s essential.
Prime power applications are where diesel generators truly shine as the primary electricity source. Remote industrial sites, construction projects, and off-grid communities throughout the Caribbean depend on these systems day in and day out. Mining operations, island resorts, and manufacturing facilities in areas with unreliable utilities all rely on prime-rated generators.
For continuous power needs, large-scale industrial operations use diesel generators to ensure uninterrupted production. When your process can’t tolerate momentary interruptions, continuous-rated generators provide rock-solid reliability.
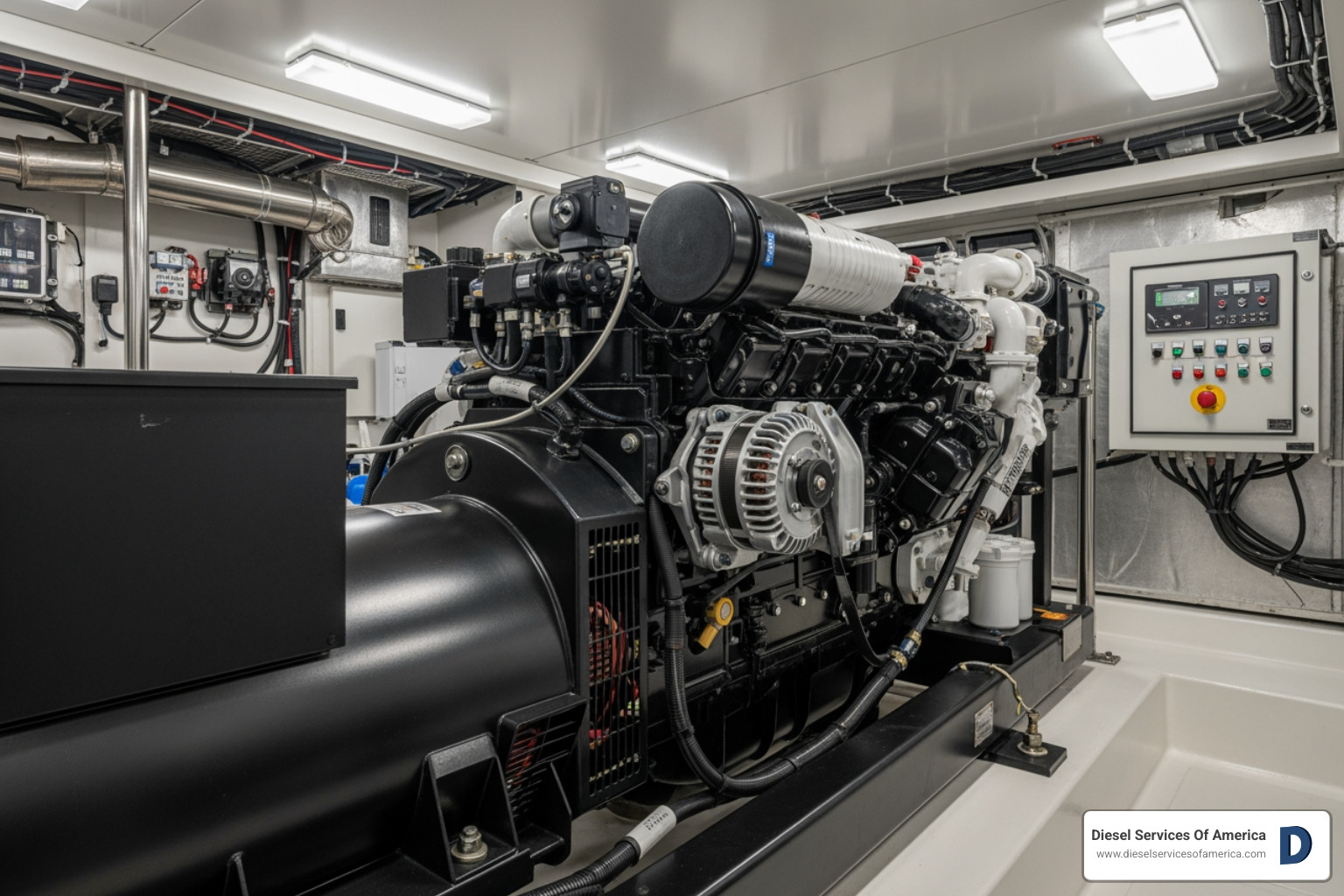

Marine applications are particularly close to our hearts here at Diesel Services Of America. On the water, reliability is a matter of safety. Marine diesel generators power everything from navigation and communication systems to refrigeration and air conditioning. Your generator keeps critical systems running when the main engine is off or provides auxiliary power while underway.
The marine environment is tough on equipment. Salt air, constant vibration, and temperature fluctuations demand generators built to withstand punishment. That’s why marine-rated units feature corrosion-resistant components and robust construction that can handle years of service in harsh conditions.
We understand these unique demands because we work with them every day in Southeast Florida’s marine industry. Learn more about our specialized offerings at Marine Diesel Generators by DSOA.
Modern Diesel Power: Efficiency, Sustainability, and Grid Integration
The story of diesel engine power generation isn’t stuck in the past—it’s evolving rapidly. Today’s diesel generators are cleaner, smarter, and more integrated with modern energy systems than ever before. For our clients operating marine vessels and industrial facilities in Southeast Florida and beyond, these advances mean more reliable power with less environmental impact.
Advantages and Limitations of Diesel Power
Let’s be honest about what makes diesel generators the go-to choice for critical power needs. When the lights go out, diesel engines start in seconds and deliver full power immediately. No warm-up period, no delays—just instant, reliable electricity when you need it most.
The power density of diesel engines is remarkable. A diesel generator produces twice the kilowatts of a comparable gas engine, making them incredibly efficient at converting fuel to electricity. Modern diesel plants operating at their sweet spot—around 65-70% loading—can generate at least 3 kWh per liter of fuel. That’s real efficiency that translates directly to lower operating costs.
Durability is another standout feature. High-quality marine and industrial diesel engines regularly run 20,000-30,000 hours before needing their first major overhaul. With proper maintenance, they can serve your facility or vessel for decades. And because diesel fuel can be stored on-site, you’re not dependent on external fuel lines during emergencies or in remote locations—a critical advantage during hurricane season in South Florida.
Of course, we need to acknowledge the challenges. Emissions have historically been a concern, though modern technology has addressed much of this issue (more on that in a moment). Depending on your installation, noise levels can require sound attenuation measures. And fuel storage demands attention—diesel needs proper conditioning to prevent degradation, and delivery can be tricky during severe weather events.
The Economics of Diesel Engine Power Generation
When you’re investing in diesel engine power generation, the sticker price is just the beginning of the story. Smart operators look at the total cost of ownership, which includes fuel consumption, maintenance schedules, and equipment lifespan.
Fuel costs represent the major portion of operating expenses. While diesel prices fluctuate with global markets, the inherent efficiency of diesel engines helps manage this expense. That 3 kWh per liter efficiency we mentioned? It reflects approximately a 30% fuel efficiency ratio—impressive for any power generation technology.
Maintenance is where many operators either save or lose money. Regular, proactive service ensures your generator runs efficiently and reaches that 20,000-30,000 hour lifespan. Skip maintenance, and you’ll face expensive repairs, reduced efficiency, and premature failure. For marine applications especially, where equipment faces harsh saltwater environments, consistent care is non-negotiable.
At Diesel Services of America, our factory-trained technicians understand the unique demands of marine and industrial diesel engines. We emphasize comprehensive maintenance schedules that maximize your uptime and minimize unexpected costs. Learn more about our approach at Diesel Engine Generator Maintenance.
Evolving Technology and Emissions Control
Here’s where the diesel engine power generation story gets exciting. The industry has undergone a remarkable change in response to environmental regulations and customer demands for cleaner operation.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has driven much of this innovation. Since 2006, EPA’s New Source Performance Standards have required new stationary diesel engines to meet increasingly stringent emission standards. The industry responded not with resistance, but with innovation.
Modern Tier 4 compliant diesel generators represent a quantum leap forward. They’re equipped with advanced after-treatment systems like Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR). These technologies drastically reduce harmful emissions—specifically nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM).
The results speak for themselves: modern prime power diesel generators emit 26 times less particulate matter than units manufactured just a decade ago. That’s not incremental improvement—that’s change.
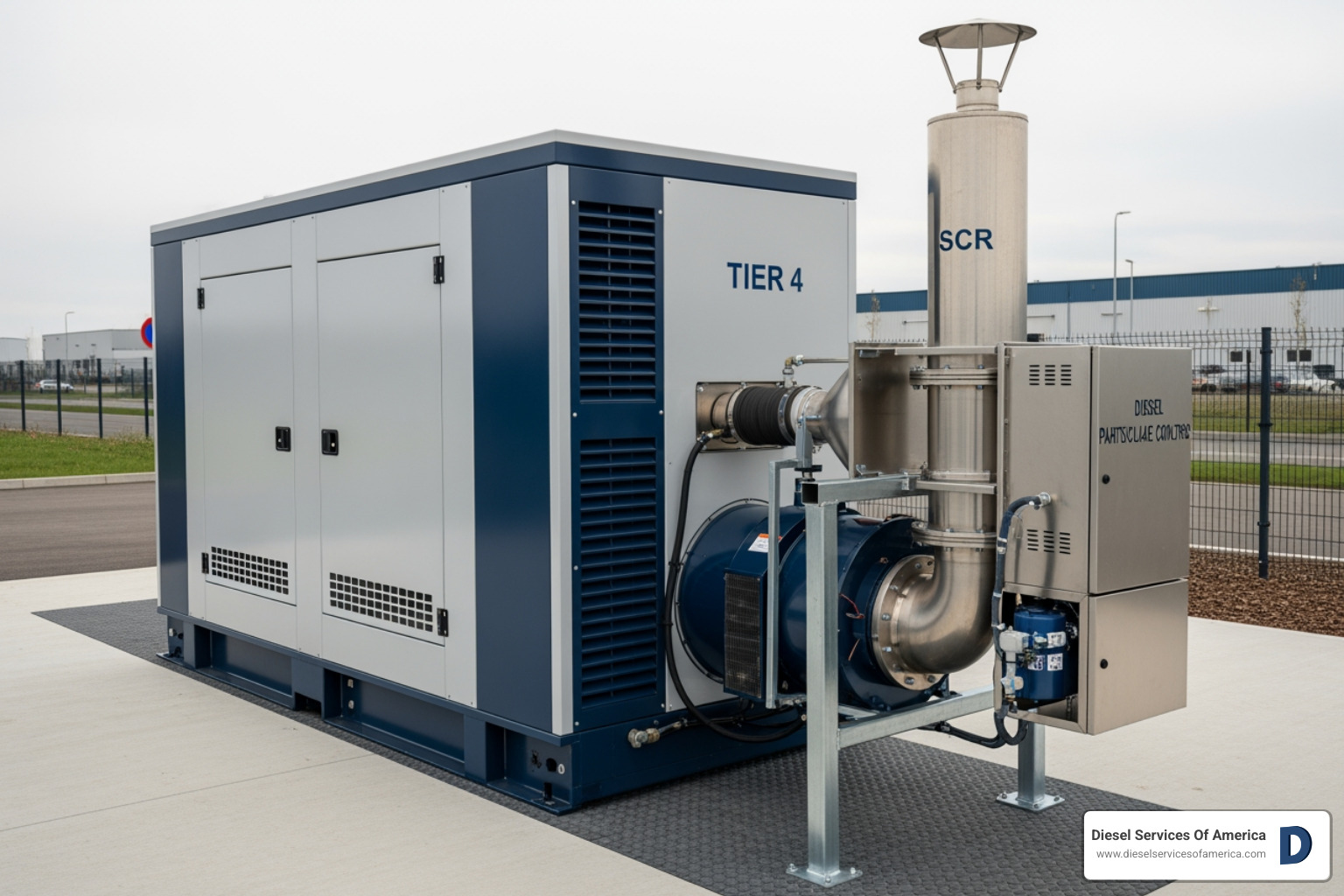

The Future of Diesel Engine Power Generation
The future of diesel engine power generation is increasingly about integration and sustainability. Diesel generators aren’t just backup power anymore—they’re active participants in modern energy systems.
Grid support is becoming a primary role for diesel generators. They can be rapidly deployed during peak demand periods, reducing strain on utility grids and preventing blackouts. This peak shaving capability saves money and increases grid reliability. Even more impressively, diesel generators provide black start capability—the ability to bring an entire utility grid back online after a total shutdown, without relying on external power sources.
Microgrid integration is another frontier. As solar and wind power become more prevalent across the Caribbean and South Florida, diesel generators serve as the reliable backbone when renewables can’t deliver. When the sun sets or the wind dies down, diesel steps in seamlessly, ensuring continuous power for critical facilities and remote communities.
Perhaps most exciting is the shift toward sustainable fuels. Renewable diesel, specifically Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil (HVO), is a true drop-in replacement for traditional diesel fuel. It can reduce your carbon footprint by 50-85% depending on feedstocks, and many modern diesel engines are already approved to run on it. No modifications needed—just cleaner operation.
This combination of advanced emission controls, grid integration capabilities, and sustainable fuel options positions diesel generators as a vital part of our energy future. They’re not the old, dirty technology some imagine—they’re evolving, adaptable, and increasingly clean power solutions.
For more insight into how diesel generators support grid stability and resilience, explore Power Solutions for Ensuring Electric Grid Reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions about Diesel Power Generation
How long can a diesel generator run continuously?
This is one of the most common questions we hear from clients in Southeast Florida, and the answer depends on a few key factors. The most important is how your generator is rated. Prime-rated and continuous-rated generators are specifically engineered for extended or even unlimited hours of operation. These workhorses can run day after day, provided they’re properly fueled and maintained.
Standby generators, on the other hand, are designed for emergency use only—think of them as your insurance policy during unexpected outages, not your primary power source. They’re built for shorter bursts of operation when the grid goes down.
The size of your fuel tank obviously plays a role too. A larger tank means longer run times between refueling, which is particularly important for marine applications or remote industrial sites where refueling isn’t always convenient.
But here’s the real secret to longevity: consistent, professional maintenance. Regular oil changes, filter replacements, and expert servicing ensure your generator can deliver its rated continuous operation without breaking down. Our Diesel Engine Generator Maintenance Service keeps your equipment running smoothly, whether you’re powering a yacht in the Caribbean or an industrial facility in Fort Lauderdale.
What are the key considerations when sizing a diesel generator?
Getting the sizing right isn’t just important—it’s absolutely critical for both efficiency and the long-term health of your generator. Under-size your unit, and you’ll overload it, causing premature wear and potential failure at the worst possible moment. Over-size it, and you’ll waste fuel and risk a problem called “wet stacking,” where unburned fuel accumulates in the exhaust system.
The first thing we look at is your total electrical load, measured in both kilowatts (kW) and kilovolt-amperes (kVA). But it’s not just about the total number—we need to understand the nature of your electrical loads. Resistive loads like lighting are straightforward, but inductive loads like motors and compressors draw significantly more power during startup than during normal operation. A motor might need three to six times its running current just to get going.
Your application type matters enormously. Are you looking for standby power that kicks in during emergencies? Prime power for a site without reliable grid access? Or continuous power for 24/7 industrial operations? Each scenario requires different sizing calculations.
Finally, we factor in your environmental conditions. High altitude reduces engine performance because the air is thinner. Hot ambient temperatures can affect cooling efficiency. Here in Southeast Florida, we understand how heat and humidity impact marine and industrial diesel generators, and we size accordingly.
Our factory-trained technicians have decades of experience calculating these precise requirements for both marine vessels and industrial facilities throughout South Florida and the Caribbean.
How have diesel generators become more environmentally friendly?
The change of diesel engine power generation over the past two decades has been nothing short of remarkable. If you’re picturing the smoky, loud diesel generators of the past, it’s time to update that mental image.
Modern diesel engines must meet strict EPA Tier 4 emissions standards, which have driven incredible innovation. Today’s generators use high-pressure common-rail fuel injection systems that atomize fuel more completely, ensuring cleaner, more efficient combustion. This technology alone has dramatically improved both performance and emissions.
Then there are the sophisticated after-treatment systems. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) uses Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) to chemically reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) by up to 90%. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) capture and burn off particulate matter—the tiny soot particles that used to be diesel’s calling card. The result? Modern prime power diesel generators emit 26 times less particulate matter than units manufactured just a decade ago.
Perhaps most exciting is the rise of sustainable fuels. Renewable diesel, also known as Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil (HVO), is a “drop-in” replacement for traditional diesel—meaning you can use it in most modern diesel engines without any modifications. Depending on the feedstock, HVO can reduce your carbon footprint by 50-85% compared to petroleum diesel, all while maintaining the reliability and power density that makes diesel the go-to choice for critical marine and industrial applications.
These advancements mean you no longer have to choose between reliability and environmental responsibility. You can have both.
Conclusion: Your Partner in Reliable Power Solutions
Whether you’re commanding a vessel through Caribbean waters or managing critical infrastructure in Fort Lauderdale, diesel engine power generation delivers the reliability you can’t afford to compromise on. We’ve walked through the science—from that first combustion cycle to the steady hum of electromagnetic induction producing usable electricity. We’ve explored how modern diesel technology has evolved to meet stricter environmental standards while maintaining the fuel efficiency and power density that made diesel the go-to choice in the first place.
The numbers tell a compelling story. Modern diesel generators emit 26 times less particulate matter than units from just a decade ago. They can run 20,000-30,000 hours before their first major overhaul. And with renewable diesel fuels, you’re looking at a 50-85% reduction in carbon footprint without sacrificing an ounce of performance.
But here’s what the numbers don’t capture: the peace of mind that comes from knowing your critical systems won’t fail. That your marine vessel’s navigation and refrigeration stay online. That your industrial facility keeps running when the grid goes down—which, as we’ve seen, happens 64% more often than it did just ten years ago.
At Diesel Services of America, we’re not just technicians—we’re your partners in keeping that power flowing. Our factory-trained experts understand the unique demands of marine and industrial diesel applications in Southeast Florida and beyond. We know that proper maintenance isn’t just about changing oil and filters. It’s about understanding your specific operational needs, environmental conditions, and power requirements. It’s about being there when you need us, whether that’s at your dock or your facility.
The future of diesel engine power generation is brighter than ever. With grid integration, sustainable fuels, and continuing technological advances, diesel generators aren’t going anywhere—they’re just getting better. And we’re here to help you steer every step of that journey.
Ready to ensure your power is always on? Contact us for marine diesel services in Southeast Florida. Because when it comes to reliable power, you deserve a partner who’s as committed to uptime as you are.

